Sustainable Architecture in Tourism Development
The Growing Importance of Sustainable Architecture in Tourism

Sustainable Practices in Global Supply Chains
The increasing awareness of environmental and social issues is driving a significant shift towards sustainable practices throughout global supply chains. Companies are recognizing that minimizing their environmental footprint and promoting ethical labor practices are no longer optional but crucial for long-term success. This includes reducing carbon emissions, minimizing waste, and ensuring fair wages and safe working conditions throughout the entire production process, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery. Sustainable supply chains are not just about reducing harm; they are about creating a positive impact on the planet and society.
Implementing sustainable practices often requires significant investment in new technologies, processes, and training programs. However, the long-term benefits, including enhanced brand reputation, increased customer loyalty, and reduced operational costs, often outweigh the initial expenses. Companies that prioritize sustainability are often seen as more responsible and trustworthy by consumers, leading to a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Environmental Impact and Resource Management
The environmental impact of global supply chains is undeniable, encompassing everything from deforestation and water pollution to greenhouse gas emissions. Recognizing this, companies are increasingly focused on minimizing their environmental footprint at every stage of the process. Strategies include optimizing transportation routes to reduce fuel consumption, implementing closed-loop systems to reduce waste, and sourcing materials from responsibly managed suppliers. This commitment to environmental stewardship extends beyond reducing immediate harm to proactively seeking ways to enhance the long-term health of the planet.
Resource management is a critical component of sustainable supply chains. Minimizing the use of scarce resources, such as water and minerals, is vital. Implementing efficient water management systems, recycling programs, and using alternative materials whenever possible are examples of these practices. This approach not only reduces environmental impact but also enhances the long-term viability of the supply chain by ensuring access to essential resources.
Social Responsibility and Ethical Labor Practices
Beyond environmental concerns, social responsibility plays a vital role in sustainable supply chains. Companies are increasingly scrutinized for their labor practices, and ethical considerations are becoming paramount. This includes ensuring fair wages, safe working conditions, and respect for human rights throughout the entire supply chain. Companies are actively working to identify and mitigate risks related to child labor, forced labor, and other forms of exploitation.
Promoting ethical labor practices fosters a positive work environment for employees and contributes to a more equitable global economy. This involves establishing transparent and traceable supply chains, fostering open communication with suppliers, and conducting regular audits to ensure compliance with ethical standards. By prioritizing social responsibility, businesses contribute to a more just and sustainable world for all.
Designing for Environmental Resilience
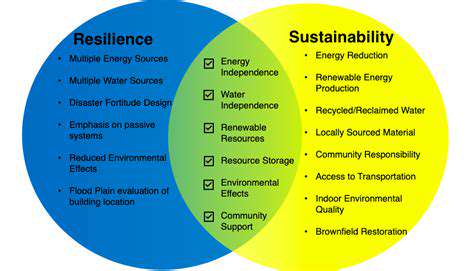
Understanding the Importance of Environmental Resilience
Designing for environmental resilience is crucial in today's world, as we face increasingly frequent and severe climate-related events. These events, from extreme weather patterns to rising sea levels, pose significant threats to infrastructure, communities, and ecosystems. Addressing these challenges requires a proactive and integrated approach that considers the interconnectedness of environmental factors and human systems. Understanding the potential impacts of climate change on specific locations is paramount in developing effective strategies for resilience.
Assessing Environmental Risks and Vulnerabilities
A thorough assessment of environmental risks and vulnerabilities is essential before any design can begin. This includes identifying potential hazards such as flooding, drought, wildfires, and extreme temperatures. Understanding how these hazards interact with existing infrastructure and social systems is equally important. By identifying these vulnerabilities early, we can design solutions that minimize potential damage and maximize the ability of the system to withstand future impacts.
Integrating Climate Change Projections into Design
Future climate projections play a critical role in anticipating potential risks and informing design decisions. These projections, combined with historical data, provide a clearer picture of the potential future impacts. Accurate predictions of future conditions allow for proactive design choices that can minimize the negative effects of climate change. For example, incorporating climate change projections into building design can lead to more sustainable and resilient structures.
Designing for Adaptability and Flexibility
Resilient design emphasizes the importance of flexibility and adaptability. Structures should be designed to accommodate potential changes in environmental conditions. This means incorporating mechanisms for future adjustments or upgrades. Flexible designs can be more cost-effective in the long run, as they can be modified to meet evolving needs and challenges.
Employing Sustainable Materials and Practices
Utilizing sustainable materials and construction practices is essential for environmental resilience. Choosing materials with low embodied carbon footprints and prioritizing renewable energy sources can significantly reduce the environmental impact of structures. Sustainable practices also contribute to the long-term health of the environment and minimize the negative effects of construction on surrounding ecosystems.
Promoting Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Effective design for environmental resilience requires collaboration between various stakeholders. This includes engineers, architects, policymakers, and community members. Sharing knowledge and best practices among these groups is crucial for developing innovative solutions. Active communication and collaboration will foster the creation of holistic and effective strategies for environmental resilience. This includes sharing data, research, and insights to inform decision-making and promote a common understanding of the challenges.
Balancing Economic Growth and Environmental Protection
Sustainable Practices in Construction
Sustainable construction practices are crucial for balancing economic growth with environmental protection. These practices encompass a wide range of strategies, from minimizing material waste and using recycled materials to employing energy-efficient building designs and incorporating green technologies. By prioritizing sustainable materials and construction methods, architects and builders can significantly reduce the environmental impact of buildings while maintaining economic viability through cost-effective solutions and resource optimization.
The selection of materials plays a significant role in the sustainability of a project. Choosing locally sourced, recycled, or renewable materials minimizes transportation emissions and reduces reliance on resource-intensive extraction processes. Furthermore, incorporating energy-efficient building materials, such as insulation and windows, can substantially lower operational costs over the lifespan of the building, demonstrating the economic advantages of sustainable choices.
Innovative Design Strategies
Innovative design strategies are paramount in achieving a balance between economic gains and environmental protection. Architects are increasingly exploring biomimicry, drawing inspiration from natural systems to create buildings that are highly efficient in energy use and resource management. This approach not only minimizes environmental impact but also fosters creativity and innovation in the design process, potentially leading to novel and aesthetically pleasing architectural solutions.
Passive design strategies, such as optimizing natural light and ventilation, are vital for reducing energy consumption. Employing these strategies in the design phase can significantly lower energy bills and reduce the carbon footprint of buildings, creating a win-win scenario for both the environment and the economy.
Economic Incentives and Policy Support
Government policies and economic incentives are essential for driving the adoption of sustainable practices in the construction industry. Implementing building codes and regulations that prioritize energy efficiency and environmental protection can encourage developers and builders to adopt sustainable practices. Financial incentives, such as tax credits or subsidies for green building materials and technologies, can further stimulate the market for sustainable architecture, making it more economically attractive for businesses and individuals.
Community Engagement and Education
Community engagement and education are critical components for promoting sustainable architecture. Educating the public about the benefits of sustainable design and construction practices can foster public support and demand for environmentally responsible buildings. Community involvement in design and construction processes can lead to more sustainable and contextually appropriate designs that meet the needs and values of the community while minimizing environmental impact. Furthermore, engaging communities in the implementation of sustainable projects can build local support and encourage long-term maintenance and care of the built environment.
Enhancing Cultural Heritage through Sustainable Design

Preserving Intangible Cultural Heritage
Intangible cultural heritage, encompassing traditions, customs, performing arts, and social practices, is often overlooked in preservation efforts. It's crucial to recognize that these aspects are vital components of a community's identity and should be actively protected. This preservation goes beyond simply documenting them; it requires actively supporting the practitioners and ensuring their traditions are passed down through generations. This includes recognizing their significance and providing resources for their continued practice.
Many intangible cultural expressions are at risk of disappearing due to modernization and globalization. Protecting them is vital for preserving the diversity of human experience and fostering cultural understanding. Efforts to document and promote these traditions can lead to a better appreciation for the richness and complexity of human creativity.
Utilizing Technology for Preservation
Modern technology offers powerful tools for preserving and sharing cultural heritage. Digital archiving allows for the creation of accessible and durable copies of historical documents, artworks, and artifacts. This ensures that these invaluable resources are not lost to decay or damage over time. The digitization of archives and libraries provides greater access for scholars, researchers, and the public, fostering a deeper understanding of the past.
Interactive online platforms can also play a significant role in engaging younger generations with their cultural heritage. Virtual museums and historical sites can bring the past to life, promoting a connection with history that might not be achievable through traditional methods. These digital tools can also facilitate cross-cultural exchange, fostering greater understanding and appreciation of diverse traditions.
Community Engagement and Ownership
Community involvement is essential for successful cultural heritage preservation. Local communities have a deep understanding of their traditions and cultural practices. Their active participation in the preservation process ensures that the heritage remains relevant and meaningful to future generations. This also fosters a sense of ownership and pride in the local culture.
Involving local communities in decision-making processes related to heritage preservation allows for a more appropriate and effective approach. This ensures that preservation efforts reflect the needs and priorities of the community. It's through such active participation that a strong sense of cultural identity is nurtured and sustained.
Promoting Cultural Tourism
Cultural tourism can be a powerful tool for preserving heritage sites and supporting local communities. The revenue generated from tourism can be reinvested into maintaining and restoring historical buildings, artifacts, and sites. This economic benefit can directly support the preservation efforts and encourage a sense of community pride.
The promotion of responsible and sustainable tourism practices is critical to ensure the long-term preservation of cultural heritage. Such practices include minimizing environmental impact and respecting local customs and traditions. This kind of responsible tourism fosters a more authentic and meaningful experience for visitors, while also benefiting local communities.
Educational Initiatives and Awareness
Educational programs play a critical role in cultivating an appreciation for cultural heritage. By incorporating heritage into school curricula and community events, we can instill a sense of pride and belonging in younger generations. This ensures the continued relevance and significance of these traditions in the modern world.
Raising public awareness about the importance of cultural heritage is crucial. This can be achieved through various initiatives, such as exhibitions, workshops, and public lectures. Increased awareness can lead to greater support for preservation efforts and a stronger understanding of the value of cultural heritage.
Read more about Sustainable Architecture in Tourism Development
Hot Recommendations
- Senior Travel Discounts and Deals
- Personalized Travel for Different Seasons and Climates
- Honeymoon Destinations: Romantic Getaways for Newlyweds
- Mythical Places: Journeys to Legendary Locales
- The Future of Travel Agents in an Automated World
- Sustainable Design for Tourist Infrastructure
- Combatting Illegal Wildlife Trade Through Travel Awareness
- The Best Beaches for Relaxation and Sunbathing
- Marine Conservation: Diving into Responsible Ocean Travel
- Measuring the Social Impact of Tourism